Power Query as a Data‑Quality Gatekeeper for Incoming Vendor Invoices
Ensuring data quality for vendor invoices is a crucial control point in accounts payable workflows. Using Power Query as a validation layer to detect duplicate invoices, identify missing fields, and catch vendor mismatches can significantly reduce audit risk and operational inefficiencies. This article explains how to implement such a validation step, providing an analytical framework for accounts payable professionals, audit specialists, and compliance technologists to maintain clean, accurate invoice datasets before payment processing.
The Critical Role of Data Validation in Invoice Processing
In today’s digital finance landscape, organizations rely heavily on automation and system integrations to accelerate invoice processing. However, automated extraction and routing do not inherently guarantee data correctness or compliance. As procurement and payment volumes increase, duplicate invoices, incomplete data fields, and vendor mismatches become prime sources of errors and fraud risks. Incorporating Power Query as a robust data quality gatekeeper allows organizations to proactively flag anomalies early, reducing manual audits and costly invoice reversals.
Building a Validation Layer within Power Query
What Power Query Brings to Invoice Validation
Power Query’s flexibility to manipulate and transform data before loading it into an ERP or accounting system positions it as an ideal platform for a pre-flight quality check. Key capabilities include:
– Importing invoice data from diverse sources (Excel, CSV, databases)
– Applying rule-based transformations and filters
– Implementing logic to identify duplicates and missing values
– Comparing vendor references against valid vendor master lists
Core Validation Components
Duplicate Invoice Detection
Duplicates often slip through manual or system checks, leading to potential overpayments. Power Query can detect duplicates by grouping on critical invoice identifiers such as:
- Invoice Number
- Vendor ID/Name
- Invoice Date
- Invoice Amount
Example approach:
- Group data by invoice number and vendor
- Filter groups with a count greater than one to flag duplicates
- Optionally, prioritize duplicates that occur within short date ranges to flag potential re-bills
Mandatory Field Completeness
Every vendor invoice should have essential fields populated to be valid for processing:
- Vendor Name and ID
- Invoice Number
- Invoice Date
- Invoice Amount
- Purchase Order Reference (if applicable)
Power Query can identify missing entries with simple conditional checks or custom columns assigning flags to records missing critical fields.
Vendor Mismatch Validation
Invoice data should be cross-verified against a vendor master list to detect unauthorized suppliers or data entry errors.
- Import a clean, trusted vendor list into Power Query
- Match vendor names or IDs in invoice records against this list
- Flag unmatched entries for further review or automated notification
Analytical Framework for Implementation
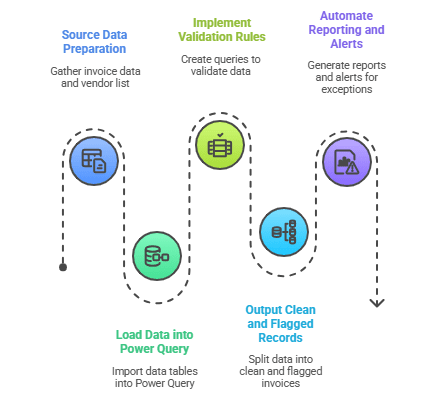
Step-by-Step Checklist
- Step 1: Source Data Preparation
Gather invoice data from your accounts payable system or scans with OCR, alongside an updated vendor master list. - Step 2: Load Data into Power Query
Import invoice and vendor data tables within Power Query in Excel or Power BI. - Step 3: Implement Validation Rules
Create duplicate grouping and filtering queries.
Add conditional columns to identify missing mandatory fields.
Perform merge/join operations to match vendors and flag discrepancies. - Step 4: Output Clean and Flagged Records
Split outputs into clean invoices ready for posting and flagged invoices needing manual intervention. - Step 5: Automate Reporting and Alerts (Optional)
Use flagged queries to generate exception reports or integrate with automated workflows for vendor follow-ups (e.g., via Power Automate).
Benefits for Audit Risk and Compliance
- Early anomaly detection: Identifies discrepancies before invoice posting.
- Automated consistency checks: Reduces manual entry errors and subjective judgments.
- Compliance adherence: Enforces company policies on valid vendors and document completeness.
- Data-driven audit trails: Provides documentation of validation logic and exceptions.
Power Query Validation Best Practices
- Maintain a Clean Vendor Master List – Regularly update and validate vendor data for accurate matching.
- Use Multiple Key Fields for Duplicates – Combine invoice number, vendor ID, and date for robust duplicate detection.
- Include Cross-Document Checks – Where possible, compare invoice data to purchase orders and receipt confirmations.
- Document Validation Rules Thoroughly – Ensure transparent audit trail for each validation step within Power Query transformations.
- Enable Automated Alerts & Reports – Leverage workflow tools to promptly action flagged invoices.
Add the validation step—cut your invoice processing time in half. Empower your accounts payable and compliance teams by embedding Power Query as a data-quality gatekeeper. This simple yet powerful integration not only reduces audit risk but also drives operational efficiency, reliability, and trust in your invoice processing workflows. Start refining your invoice pipeline today and transform how your finance function handles vendor data quality.
Learn more about how you can use power query here. Access these curated notes on Microsoft to get started – What is Power Query? & Power Query Documentation
